The Immunizations guideline implements the complete breadth of current CDC recommendations for childhood and adult immunizations. It includes scenarios for The Neonate and for Primary Care. It also includes a Population Immunization Surveillance scenario that can survey a large population of patients.
All the details of the encoding in Protégé for Immunizations have been generated as a web page [here].
These three scenarios are just the beginning. This guideline could have several additional scenarios, for example:
- All patients seeking service in the emergency department or urgent care facility have reminders issued for vaccines.
- All patients being discharged from the hospital have vaccine requirements reviewed and alerts issued.
- The home health visitor has automated alerts generated for the scheduled list of patients who are due for vaccinations.
- The long term care facility is issued automated orders verifying eligibility for overdue vaccinations.
This guideline exemplar uses 628 Criteria in 8 Recommendation Sets with 37 Decision Nodes, 7 Context Nodes, and 58 Action Nodes.
| Scenarios | Vocabulary | Logic |  top top |
|
|||
- SCENARIO 1: Hepatitis B immunization for hospitalized newborns
-
A baby is admitted to the nursery in a local hospital following birth in the L&D suite. The admission event triggers the SAGE engine, which checks for vaccination eligibility against the child's and mother's clinical records and then takes appropriate action.
- Determines whether Hepatitis B vaccine is due, notifies provider to inquire about illness and obtain consent, checks deferral reasons, and places the order for the Hepatitis B vaccine.
- Determines whether follow up serologic lab tests are needed for infants at risk and places the orders to be collected at nine months of age.
- Determines whether Hepatitis B Immune Globulin is due and places orders.
- Checks maternal record for presence of Hepatitis B serologic status, orders HBsAg lab test if status is unknown, generates a time drive event to recheck maternal HBsAg results every 12 hours until infant is 24 hours old.
- SCENARIO 2: Immunization Practice in Primary Care Setting
-
Patient arrives at primary care clinic requesting care. The patient is checked in and is then met by the clinic nurse. The nurse initiates the encounter by logging onto the clinic information system (CIS) and selecting the patient record. SAGE is triggered and an evaluation of the patient's immunization needs is begun. Final recommendations for immunizations due are delivered to provider's inbox.
- Determines eligibility for immunizations based on age and patient characteristics
- Computes immunizations due based on eligibility criteria
- Checks for contraindications and sends notification to provider of 'due but contraindicated' vaccines
- Identifies 'due' immunizations and sends request to provider to inquire about illness and obtain immunization consent. Vaccine information sheets (VIS) for due immunizations are generated to print providing the patient / parent current immunization information from the Center for Disease Control (CDC)
- Checks clinical record for deferral reasons and removes deferred immunizations from recommendations
- Places automated orders in the CIS for immunizations due
- SCENARIO 3: Managing immunizations for a population of patients
-
Every Sunday at midnight, a background batch program starts within the clinical information system (CIS) for a outpatient health clinic. The program checks the patient records of all patients enrolled in the immunization guideline for immunization eligibility. The patient record is reviewed for immunization history, all data pertinent to eligibility criteria and contraindications for immunizations. It identifies all patients who are due for immunizations and generates a report for the clinic manager who coordinates the scheduling by means of phone contact or postcard notification.
- Initiates a weekly or real time batch program to determine immunization eligibility for a population of patients
- Determines eligibility for vaccines based on age and patient characteristics
- Checks for contraindications to immunizations due
- Generates list of patients eligible for immunizations
| Scenarios | Vocabulary | Logic |  top top |
|
|||
Here are examples of the standard terminology used in this guideline, organized by Virtual Medical Record (VMR) class. In each class, there will be terms of different types. For example, to describe an allergic reaction, one needs the allergen, the type of reaction, and the severity of that reaction. Here we see codes from SNOMED Clinical Terms (SNOMED CT), and Logical Observation Identifiers Names and Codes (LOINC®), NDF-RT, and International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision (ICD-9).
The project maintains SAGE-defined concepts in separate SAGE terminologies that are linked to existing standard terminologies if the SAGE concept is either derived from or should be an addition to the external standard. For example if a SAGE concept was defined as a collection of LOINC concepts, it is maintained as a member of the SAGE LOINC terminology. If a concept's intent is consist with a particular terminology's intent, such as SNOMED CT and is a reasonable candidate for inclusion in a future release, it is maintained in the appropriate SAGE-linked terminology, such as SAGE SNOMED CT.
The concepts listed here are examples of the coded values used in each of the Virtual Medical Record classes. They are NOT examples of the class instances themselves. For example, Adverse Reactions requires a substance, like B-lactam, and a reaction type like Anaphylaxis. So, both concepts would show up under Adverse Reaction.
The Immunizations Guidelines uses 201 concepts:
| VMR Class | Number of Concepts |
|---|---|
| AdverseReaction | 35 |
| MedicationOrder | 5 |
| Observation | 61 |
| Problem | 72 |
| SubstanceAdministration | 27 |
| VMROrder | 4 |
- AdverseReaction 4 of 35
- Immunologic reaction function [SNOMED CT 56393004]
- Anaphylaxis [SNOMED CT 39579001]
- Guillain Barre [SNOMED CT 40956001]
- Hepatitis A virus vaccine [SNOMED CT 14745005]
- MedicationOrder 5 of 5
- Inhaled steroid preparation [SAGE SNOMED CT C56]
- Hepatitis B vaccine pediatric 5micrograms/0.5mL prefilled syringe [SNOMED CT 333571009]
- Varicella virus vaccine live 1350pfu/0.5mL powder [SNOMED CT 377008002]
- Salicylate product [SNOMED CT 350312004]
- Intranasal influenza live virus vaccine 0.5mL [SNOMED CT 409270000]
- Observation 7 of 61
- Heterosexual [SNOMED CT 20430005]
- Immunization consent given [SNOMED CT 310375005]
- RUBELLA VIRUS AB.IGG:ACNC:PT:SER:ORD: [LOINC 25514-1]
- HEPATITIS B VIRUS SURFACE AG:ACNC:PT:SER:ORD [LOINC 5195-3]
- IPV Vaccine is due [SAGE C117]
- DT Vaccine is deferred [SAGE C133]
- Day care worker (occupation) [SAGE SNOMED CT C35]
- Problem 5 of 72
- Herpes zoster [SNOMED CT 4740000]
- Hyposplenism [SNOMED CT 23761004]
- Patient currently pregnant [SNOMED CT 77386006]
- Chronic renal failure syndrome [SNOMED CT 90688005]
- Untreated active tuberculosis [SAGE SNOMED CT C59]
- SubstanceAdministration 5 of 27
- Hepatitis A virus vaccine [SNOMED CT 14745005]
- Inactivated poliovirus vaccine [SNOMED CT 125688000]
- Diphtheria vaccine [SNOMED CT 333536009]
- Antimetabolite [SNOMED CT 58760003]
- Glucococorticoid preparation (product) (parenteral and oral forms) [SAGE SNOMED CT C54]
- VMROrder 4 of 4
- Hepatitis B surface antigen level [SNOMED CT 315131000]
- Contraindicated [SNOMED CT 410536001]
- Hepatitis B core antibody level [SNOMED CT 315133002]
- week [SNOMED CT 258705008]
| Scenarios | Vocabulary | Logic |  top top |
|
|||
Guideline Logic Flow for Neonatal Hepatitis B Immunization |
The triggering event, admission to the hospital, initiates the Neonatal Hepatitis B recommendation set. A precondition for guideline enrollment is age less than 7 days. After meeting age criterion, the decision 'Is Hepatitis B vaccine due?' is evaluated. Eligibility criteria for Hepatitis B immunization are queried within the CIS. Strict rule-in criteria include:
- reactive maternal hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) serologic test
- infant is > 24hrs of age and maternal HBsAg status is unknown
- infants weight is ≥ 2kg
A positive evaluation of one of the above criteria and no record of Hepatitis B immunization exists dictates that the immunization is 'possibly due' and sends an inbox notification to the provider to inquire about illness and to obtain parental consent. Contraindications to the vaccine are then evaluated.
'Is there reason to defer Hepatitis B Vaccination' is the subsequent decision node, evaluating the provider response to patient related inquiries. If no deferral reasons are identified, an order for the immunization is sent to the provider inbox via a SAGE message.
The guideline sequentially evaluates the Hepatitis B surface antigen
(HBsAg) serologic status of the neonate's mother.
Strict rule-in criteria are:
- infant's age less than 24 hours old
- maternal HBsAg has not been measured in the past 9 months
- current maternal order for HBsAg does not exist within the CIS
- maternal problem of HBsAg positive does not exist
- neonate problem 'Maternal HBsAg reactive' does not exist
If all rule-in criteria evaluate to 'true', then a stat order for maternal HBsAg is generated. An automatic event is generated to monitor the result of the maternal HBsAg result every 12 hrs until the infant is > 24 hours of age.
The guideline evaluates whether future Hepatitis B laboratory tests
are required for the neonate.
Strict rule-in criteria are:
- reactive maternal HBsAg serologic test
- absence of maternal HBsAg testing
- maternal problem: HBsAg reactive
- neonatal problem: Maternal HBsAg reactive
A positive evaluation of one of the criteria will generate orders for Hepatitis B surface antigen and Hepatitis B core antibody levels at 9 months of age.
The guideline further evaluates the need for Hepatitis B Immune
Globulin.
Strict rule-in criteria are:
- reactive maternal HBsAg serologic test
- maternal problem: HBsAg reactive
- neonatal problem: Maternal HBsAg reactive
- infant is > 24hrs of age and maternal HBsAg status is unknown
A positive evaluation of any one of these criteria will generate orders for Hepatitis B Immune Globulin for the infant.
Guideline Logic Flow for Primary Care Immunizations |
|
The triggering event, 'outpatient nurse accesses the patient record' initiates the primary care clinic immunization recommendation set. The Eligibility Master Subguideline determines eligibility by patient age. The Pediatric Immunization Subguideline evaluates all patients < 19 years of age. The Adult Immunization Subguideline evaluates patient >= 19 years of age.
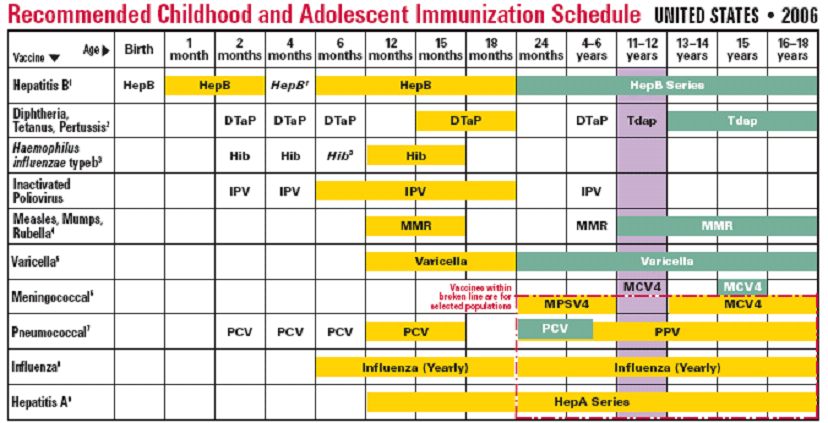
Each subguideline evaluates criteria specific to each vaccine to determine eligible immunizations for the patient. Here is the schedule for immunizations of children from the Center for Disease Control. This is the basis for the schedule expressed in our subguideline for children.
The patient record is then checked for any contraindications. Notifications are sent to the provider inbox for 'due but contraindicated' vaccines. For all other due vaccines, a request is sent via inbox message to the provider to inquire about illness and obtain immunization consent.
Vaccine information sheets (VIS) for due immunizations are generated to print providing the patient / parent current immunization information from the Center for Disease Control (CDC). The guideline queries the CIS for deferral reasons and removes any deferred immunizations. Pending orders for the due immunizations are placed in the CIS and a notification is sent to the provider's inbox.
Immunization recommendations change with time. For example in 2006, we updated our encoding to include
- Varicella: 2 dose recommendation for all ages (August 2006)
- HPV: 3 dose series for females ages 9-26 (August 2006)
- Tdap:
Use in pregnant women (August 2006)
Use in adult population (March 2006)
Here is an example of a set of rules about Pediatric Polio Vaccine from one of the working documents.
Recommendation set: Pediatric Polio vaccine Contraindication to Polio::= anaphylactic reaction to Polio vaccine OR anaphylactic allergy to neomycin OR anaphylactic allergy to polymyxin B OR anaphylactic allergy to streptomycin Reason for deferral::= Patient acutely ill by judgment of care provider OR Patient is pregnant Rule 1: First dose IF NO CONTRAINDICATION TO POLIO AND NO REASON FOR DEFERRAL AND NUMBER OF POLIO VACCINE DOSES = 0 AND AGE 6 ≥ WEEKS THEN ADVISE INACTIVATED POLIO VACCINE IS DUE Rule 2: Second dose IF NO CONTRAINDICATION TO POLIO AND NO REASON FOR DEFERRAL AND NUMBER OF POLIO VACCINE DOSES = 1 AND TIME SINCE LAST POLIO ≥ 4 WEEKS THEN ADVISE INACTIVATED POLIO VACCINE IS DUE Rule 3: Third dose IF NO CONTRAINDICATION TO POLIO AND NO REASON FOR DEFERRAL AND NUMBER OF POLIO VACCINE DOSES = 2 AND TIME SINCE LAST POLIO ≥ 4 WEEKS THEN ADVISE INACTIVATED POLIO VACCINE IS DUE Rule 4: Fourth dose IF NO CONTRAINDICATION TO POLIO AND NO REASON FOR DEFERRAL AND NUMBER OF POLIO VACCINE DOSES = 3 AND TIME SINCE LAST POLIO ≥ 4 WEEKS AND (NOT ((ALL DOSES ORAL) OR (ALL DOSES IPV))) AND (AGE AT LAST POLIO > 4 YEARS) THEN ADVISE INACTIVATED POLIO VACCINE IS DUE
Guideline Logic Flow for Population Management |
|
The triggering event for the Population Management Recommendation Set is a predetermined time specification (e.g. 'every Sunday night at midnight') or an 'on demand' request to initiate the recommendation set.
The Eligibility Master Subguideline is triggered which evaluates the patient initially by age. The Pediatric Immunization Subguideline evaluates all patients < 19 years of age. The Adult Immunization Subguideline evaluates patient >= 19 years of age. Each subguideline evaluates criteria specific to each vaccine to determine eligible immunizations for the patient. The guideline then checks each due vaccine for any contraindications. A report identifying immunizations due for each patient in the source population is generated.
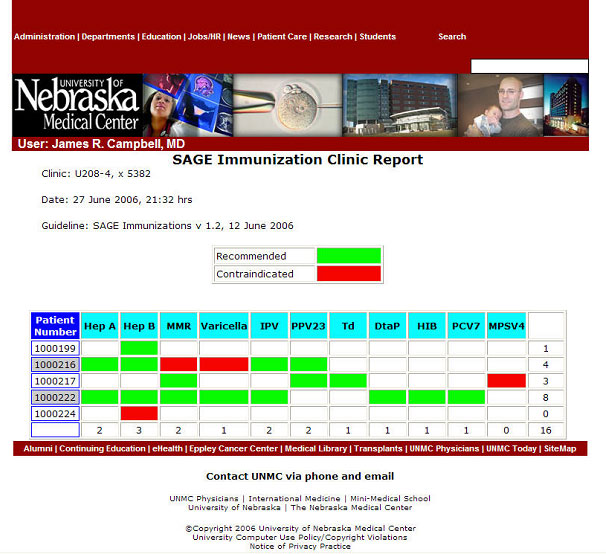
Here is an example of population report generated for a small clinic, displayed on the web, at the University of Nebraska.

 Scenarios
Scenarios